In the 1980s Michael Porter taught us the importance of competition and industry analysis (Porter´s five forces analyses). Nowadays, we are facing a demand crisis, overcapacity, new incumbents from technology firms, industry barriers are falling, and so on. Thus, continue monitoring competition, the industry and reviewing our business model is getting mandatory. Let’s review how the business landscape is changing so fast and affecting almost every industry.
Reviewing some of the major changes affecting to the 7 Types of Business
John Tenenent in his book Financial Management: Principles and Practice developed a simple but powerful 7 Types of Business framework to define the seven broad categories of business according to products and services to be provided. We are using this model to check how many business types are affected for new players or companies using new business model that challenges the current industry status quo.
The 7 Types of Business (adapted from: Tenenent, John "Financial Managemet: Principles and Practice)
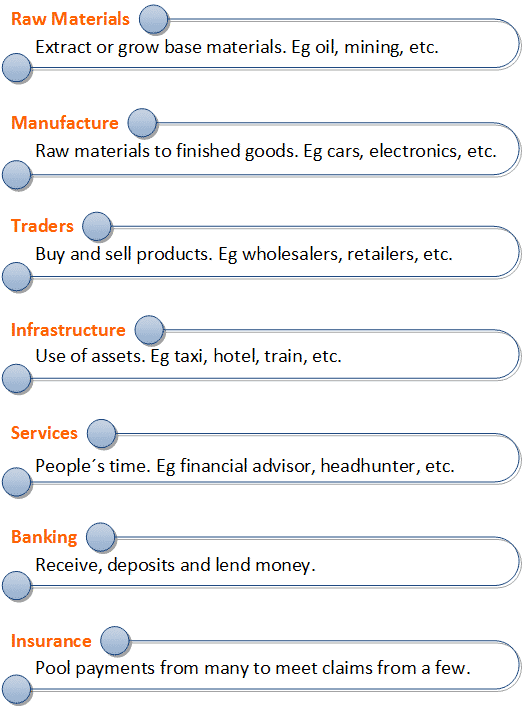
We are going to review quickly a few examples of how all of those seven types of business without any exception are being already challenge. This could create an important stream of turnarounds, if companies do not transform themselves before:
1. Raw materials: Companies need to find better and cheaper raw materials to maintain their differentiation or low cost advantage.
- Oil prices are mainly affected for the current overproduction that does not match with demand. However, there are other factor that we should consider regarding the future of oil industry. Eg. fracking technology improvements, renewable energy (substitutes), or the electric car.
- Lithium batteries consume a huge amount of lithium, but graphene could be the next material for batteries.
2. Manufacture: Automation and the use of robots will continue to be a key Success Factor to rise competitiveness.
- Vehicle manufacturer: It looks those technology companies like Google and Apple would like to take a portion of the automotive industry developing for instance their own self-driving cars. The electric car is a disrupting technology bringing new incumbents as Tesla. Another trend in this industry is buying smaller cars with less initial and maintenance cost and more environmentally friendly. Finally, we have to mention the new trend in developed countries to rent car when the use is not very intensive. So Daimler has decided to jump on this related industry with their tiny SMART electric cars (go2car.com).
- Hardware manufacturer: The cloud concept will move massive sales from many corporate customers that today buy from companies like HP or Dell to a few companies (Google, Microsoft, Amazon, etc.) managing huge data centers. Additionally, end users will require less powerful devices like chromebooks to run cloud applications rather than the expensive traditional computer based on.
- GPS: The massive penetration of mobiles and free GPS applications like Google Maps are massively affecting the demand GPS devices from firms like TomTom.
3. Traders: Manufacturers are selling directly to end customers (disintermediation) to improve end customer control and margins.
- Wholesaler: The traditional wholesaler function continue to be reduced by the more flexible solution that Logistics Service provider can offer.
- Retailer: Customers buying by Internet directly to manufacturers have access to the complete portfolio of products and sizes, and receive the items at home or office comfortably. Amazon is entering the Logistics Service provider business and they are offering those services plus retail services with their own web site.
4. Infrastructure: There are some Internet companies taking advantage of private vehicles or apartments underused to offer extra income to owners, and good rates to end customers.
- Taxi: Uber used to offer around 30% cheaper prices than traditional taxis, AND much better service because it is more secure this service that register the taxi driver (this is an important differentiator in some countries where security is an issue), vehicles have and use air conditioner (underdeveloped countries have an important amount of taxis without AC, and in developed countries they have AC but the driver many times decide to switch off to save fuel), the customer service is better (Uber vehicles have sweets, water, and service is evaluated after trips to guarantee the best service level).
- Public transportation: BlaBlaCar connects people without car who needs to travel with people traveling with their own vehicle who has empty seats. That means for people without car savings around 50% compared with bus or train rates. Additionally, those trips used to be faster, more comfortable, and leave you in a more convenient location.
- Hotels: Airbnb is an alternative to traditional hotels.
- Telecoms: It looks that soon telecom main service will be Internet access because almost 100% of calls and SMS will be performed from applications based on Internet (Whatsapp, Skype, etc.)
5. Services: Many services are based on information and-or knowledge. Internet is offering access to people in an easier and cheaper way to get that information or knowledge from applications (Linkedin to find employees/job, etc.). Thus, the value perceived of those traditional services is getting lower.
- Software development: In the past being the leader Operative System owner was a huge competitive advantage in the software industry. Nevertheless, with the disruption of cloud computing it does not matter, if people access to cloud application with a Windows, Mac or Chrome.
6. Banking: Strong pressure to reduce traditional offices and move physical processes performed by people to virtual/electronics ones in order to maintain contribution margins higher than 10%. Moreover, new incumbent from FinTech startups are coming.
- Credit cards: There are more than ten large mobile payment initiatives threaten the credit cards sub-industry, and some of them are commanded for important technology firms like Google, Apple or Samsung.
- Banks: There are many pure Internet banks taking advantage of their low cost structure to offer traditional banking services but with less commissions. Imagin bank just operates on mobiles what pushed the bank to create lean customer facing processes, and will bring better efficiencies.
- Investment house: There are some companies (eg. Wealthfront) starting to offer computer efficient investment advice rather than traditional investment advisor recommendations.
7. Insurance: Pure Internet insurer are facing an important low cost competitive advantage (less offices, “no sales force”, automatic risk review processes, etc.) E.g. Verti.com in Spain (a MAPFRE company), or Zhong An in China. Another interesting example for the insurance business “revolution” is Zenefits that provide free cloud-based HR software when companies use Zenefits purchasing power to buy their health insurance, or to choose a payroll provider, or other service.
What are main trends of new incumbents in the different industries?
- Internet continues moving on from being just a sales channel for traditional companies to be a more efficient business model for new incumbents.
- New Sales Efficient Supply Chain Management models: For instance, the largest retailer in Spain is Mercadona that removed all the items without at least one unit being sold in all the stores every day. So they can have many small and medium supermarkets with items of high turnover which means good prices for customers and good profitability for the company (for more details see our post “Sales Efficient Supply Chain Management (SESCM): A Success Foundation for a Business Model”).
- Innovation firms like Alphabet have born to take advantage of the huge innovation opportunities in many industries. Those really innovation firms are taking advantage of the slow reaction of traditional firms in some cases leading for people who does not properly understand the new technology revolution, or they are too much focus on their traditional industry business model.
- Pricing model is on the top of the business model: Business models must create value for customers, and lucre/profit used to be one of the most important purchasing motives. So we can see companies like Uber taking advantage of idle time of people and their cars to be able to offer at least 30% cheaper rates than taxis. Zenefits is another example selling HR software for “free.”
- Industry entry barriers are falling: For instance, Google and Apple are “thinking/preparing” to enter the automotive industry, while Mercedes Benz is entering the car rental industry with the initiative car2go.com, and so on.
- Some traditional business are disappearing: The printing industry is suffering the impact of electronic books, screens for ads, the use of Internet for marketing communication. Plastic bag manufacturers are suffering the strong campaign of retailers not to use those items for “environmental reasons” and cost reduction. Etc.
- Unicorn firms (current private startup companies valued at $1B and above). The financial support of those firms that could make a revolution in their industry are massive (at the time of writing this post is a total cumulative valuation of $556B).
Should we expect a higher number of turnaround and transformation initiatives in the short and medium term?
There are some studies that analyze why firms are failing, and what are the signs of a troubled business. Those studies used to highlight some management, financial and control issues. However, very soon we will probably see that a new business failure cause will be obsolete business model.
There are some industries that they have received the wake-up call. For instance the banking industry is involved in the digital transformation. However, I would like to stress that digital transformation is just one of the “must be” transformations. There are others 7 key transformation (growth, sales force, customer experience, supply chain, procurement, lean and culture transformation) with much less media impact but those are essential too to survive after the present amazing and turbulent business environment.
